Gdp Can Be Calculated by Summing Up the "Value Added" at Every Stage of Production.
Defining GDP
Gross domestic product is the market value of all final appurtenances and services produced within the national borders of a country for a given period of time.
Learning Objectives
Distinguish between the income and expenditure approaches of assessing Gdp
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- Gdp can be measured using the expenditure approach: Y = C + I + Chiliad + (X – Thou).
- GDP tin can exist adamant by summing up national income and adjusting for depreciation, taxes, and subsidies.
- Gross domestic product can be determined in two ways, both of which, in principle, give the same result.
Fundamental Terms
- Gross domestic product: Gross domestic product (Gdp) is the marketplace value of all officially recognized terminal goods and services produced inside a state in a given period of time.
Gross domestic product (Gdp) is the market place value of all last appurtenances and services produced within the national borders of a country for a given menses of time. GDP can exist determined in multiple ways. The income approach and the expenditure approach highlighted below should yield the aforementioned last Gdp number.

Elementary view of expenditures: In an economy, households receive wages that they so use to buy last goods and services. Since wages somewhen are used in consumption (C), the expenditure approach to calculating GDP focuses on the end consumption expenditure to avert double counting. The income arroyo, alternatively, would focus on the income made past households as one of its components to derive GDP.
Expenditure Approach
The expenditure arroyo attempts to calculate GDP by evaluating the sum of all concluding expert and services purchased in an economic system. The components of U.S. Gdp identified equally "Y" in equation course, include Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government Spending (G) and Cyberspace Exports (X – M).
Y = C + I + G + (10 − M) is the standard equational (expenditure) representation of Gdp.
- "C" (consumption) is normally the largest Gross domestic product component in the economy, consisting of private expenditures (household final consumption expenditure) in the economic system. Personal expenditures fall nether one of the following categories: durable goods, non-durable goods, and services.
- "I" (investment) includes, for instance, business concern investment in equipment, simply does not include exchanges of existing assets. Spending by households (non regime) on new houses is also included in Investment. "Investment" in GDP does non mean purchases of fiscal products. It is of import to note that buying financial products is classed as ' saving,' as opposed to investment.
- "G" ( government spending ) is the sum of government expenditures on final appurtenances and services. Information technology includes salaries of public servants, purchase of weapons for the military, and any investment expenditure by a government. However, since Gdp is a measure of productivity, transfer payments fabricated by the government are not counted considering these payment do not reflect a purchase by the government, rather a motion of income. They are captured in "C" when the payments are spent.
- "X" (exports) represents gross exports. Gdp captures the amount a state produces, including goods and services produced for other nations' consumption, therefore exports are added.
- "One thousand" (imports) represents gross imports. Imports are subtracted since imported goods will exist included in the terms "K", "I", or "C", and must be deducted to avoid counting foreign supply as domestic.
Income Approach
The income approach looks at the final income in the country, these include the post-obit categories taken from the U.Southward. "National Income and Expenditure Accounts": wages, salaries, and supplementary labor income; corporate profits interest and miscellaneous investment income; farmers' income; and income from not-farm unincorporated businesses. Two not-income adjustments are made to the sum of these categories to make it at GDP:
- Indirect taxes minus subsidies are added to go from factor cost to marketplace prices.
- Depreciation (or Capital Consumption Allowance) is added to get from net domestic product to gross domestic product.
Learning from Gdp
Gdp is a measure of national income and output that can be used as a comparing tool.
Learning Objectives
Explicate how Gross domestic product is calculated.
Central Takeaways
Key Points
- The output approach focuses on finding the total output of a nation by straight finding the total value of all goods and services a nation produces.
- The income approach equates the total output of a nation to the total cistron income received by residents or citizens of the nation.
- The expenditure approach is basically an output accounting method. It focuses on finding the total output of a nation by finding the full amount of coin spent.
Cardinal Terms
- gross national production: The total market value of all the goods and services produced by a nation (citizens of a country, whether living at dwelling house or abroad) during a specified flow.
- gross domestic product: A measure of the economic production of a particular territory in fiscal upper-case letter terms over a specific time period.
There are two commonly used measures of national income and output in economics, these include gdp ( Gross domestic product ) and gross national product (GNP). These measures are focused on counting the total amount of goods and services produced within some "boundary" where the boundary is defined by either geography or citizenship.
Since GDP measures income and output, information technology can exist used to compare two countries. The country with college GDP is frequently regarded as wealthier, but, when using GDP to compare countries, information technology is of import to recall to adjust for population.
GDP
GDP limits its focus to the value of goods or services in an bodily geographic boundary of a state, where GNP is focused on the value of goods or services specifically owing to citizens or nationality, regardless of where the production takes place. Over time GDP has become the standard metric used in national income reporting and nearly national income reporting and country comparisons are conducted using Gdp.
Gdp can be evaluated by using an output arroyo, income approach, or expenditure arroyo.
Output Approach
The output arroyo focuses on finding the total output of a nation by directly finding the total value of all goods and services a nation produces. Because of the complication of the multiple stages in the production of a adept or service, but the final value of a good or service is included in the full output. This avoids an issue referred to equally double counting, where the total value of a adept is included several times in national output, by counting it repeatedly in several stages of production.
For example, in meat production, the value of the expert from the subcontract may be $10, then $30 from the butchers, so $60 from the supermarket. The value that should exist included in final national output should be $threescore, not the sum of all those numbers, $ninety.
Formula: Gdp (gross domestic production) at market place price = value of output in an economy in the item year – intermediate consumption at cistron cost = Gross domestic product at market place price – depreciation + NFIA (net factor income from abroad) – net indirect taxes.
Income Approach
The income approach equates the total output of a nation to the total factor income received by residents or citizens of the nation. The main types of factor income are:
- Employee compensation (price of fringe benefits, including unemployment, health, and retirement benefits);
- Interest received cyberspace of interest paid;
- Rental income (mainly for the use of real manor) internet of expenses of landlords;
- Royalties paid for the apply of intellectual holding and extractable natural resources.
All remaining value added generated by firms is called the residual or profit or business greenbacks flow.
Formula: GDI (gross domestic income, which should equate to gross domestic product) = Compensation of employees + Net involvement + Rental & royalty income + Business cash catamenia
Expenditure Approach
The expenditure approach is basically an output bookkeeping method. It focuses on finding the total output of a nation by finding the total corporeality of money spent. This is acceptable, considering like income, the full value of all appurtenances is equal to the total amount of coin spent on goods. The basic formula for domestic output takes all the unlike areas in which coin is spent within the region, so combines them to observe the total output.

U.Due south. Gross domestic product Components: The components of Gdp include consumption, investment, government spending, and cyberspace exports (exports minus imports).
Formula: Y = C + I + G + (X – M); where: C = household consumption expenditures / personal consumption expenditures, I = gross individual domestic investment, G = regime consumption and gross investment expenditures, X = gross exports of goods and services, and M = gross imports of goods and services.
The Circular Menstruation and Gross domestic product
In economic science, the "circular flow" diagram is a simple explanatory tool of how the major elements in an economy interact with i some other.
Learning Objectives
Evaluate the effect of the circular flow on GDP
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- In the circular flow model, the household sector, provides diverse factors of production such equally labor and capital, to producers who in turn produce appurtenances and services.
- Firms provide consumers with goods and services in exchange for consumer expenditure and "factors of production" from households.
- Investment is equal to savings and is the income non spent but available to both consumers and firms for the purchase of capital investments, such as buildings, factories and homes.
- A portion of income is also allocated to taxes (income is taxed and the remaining is either consumed and or saved); government spending, One thousand, is based on the tax revenue, T.
- The continuous flow of product, income and expenditure is known as circular flow of income; it is circular because it has neither whatever kickoff nor an end.
Key Terms
- Factors of production: In economics, factors of production are inputs. They may as well refer specifically to the master factors, which are stocks including land, labor, and capital appurtenances practical to product.
- circular menstruum: A model of market economy that shows the flow of dollars between households and firms.
In economics, the "round menses" diagram is a simple explanatory tool of how the major elements as defined by the equation Y = Consumption + Investment + Government Spending + ( Exports – Imports). interact with one another. Circular catamenia is basically a continuous loop that for any point and fourth dimension yields the value "Y" otherwise defined as the sum of last skillful and services in an economy, or gross domestic product ( GDP ).

Circular flow: The circular flow is a simplified view of the economic system that provides an ability to assess GDP at a specific point in fourth dimension.
In the circular catamenia model, the household sector, provides diverse factors of product such as labor and capital, to producers who in turn produce goods and services. Firms compensate households for resource utilized and households pay for goods and services purchased from firms. This portion of the circular flow contributes to expenditures on consumption, C and generates income, which is the basis for savings (equal to investment) and government spending (tax revenue generated from income).
Investment, I, is equal to savings and is the income not spent but available to both consumers and firms for the purchase of capital letter investments, such as buildings, factories and homes. I represents an expenditure on investment capital letter.
Income generated in the relationship between firms and households is taxed and the remaining is either consumed and or saved. Government spending, G, is based on the revenue enhancement acquirement, T. Thou tin can exist equal to taxes, less than or more than than the tax revenue and represents authorities expenditure in the economy.
Finally, exports minus imports, Ten – M, references whether an economy is a net importer or exporter (or potentially trade neutral (X – M = 0)) and the impact of this component on overall Gross domestic product. Note that if the country is a internet importer the value of X – M will exist negative and will accept a downward bear upon to overall Gdp; if the country is a net exporter, the opposite will be truthful.
Circular menstruation
The continuous flow of product, income and expenditure is known as circular period of income. It is circular because information technology has neither whatsoever beginning nor an end. The circular flow involves two bones assumptions:
1. In any commutation process, the seller or producer receives what the buyer or consumer spends.
2. Goods and services flow in ane direction and money payment menstruum in the contrary or return direction, causing a circular period.
Gross domestic product Equation in Depth (C+I+Thousand+X)
Gross domestic product is the sum of Consumption (C), Investment (I), Regime Spending (1000) and Net Exports (X – One thousand): Y = C + I + G + (10 – M).
Learning Objectives
Place the variables that brand upwards GDP
Cardinal Takeaways
Central Points
- C ( consumption ) is normally the largest Gdp component in the economy, consisting of individual (household final consumption expenditure ) in the economy.
- I ( investment ) includes, for instance, business investment in equipment, but does not include exchanges of existing avails.
- G ( government spending ) is the sum of government expenditures on final goods and services. It includes salaries of public servants, purchase of weapons for the armed forces, and any investment expenditure by a government.
- Ten ( exports ) represents gross exports. Gross domestic product captures the amount a country produces, including goods and services produced for other nations' consumption, therefore exports are added.
- G (imports) represents gross imports.
Primal Terms
- government spending: Includes all regime consumption, investment but excludes transfer payments made by a state.
- consumption: In the expenditure arroyo, the amount of goods and services purchased for consumption by individuals.
- consign: Any good or article, transported from ane land to another country in a legitimate fashion, typically for use in trade.
- import: To bring (something) in from a foreign country, especially for sale or trade.
- investment: A placement of capital in expectation of deriving income or turn a profit from its use.
Gross domestic product (Gdp) is defined equally the sum of all goods and services that are produced within a nation's borders over a specific fourth dimension interval, typically 1 calendar yr.
Components of GDP
GDP (Y) is a sum of Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government Spending (G) and Net Exports (10 – M):
[latex]Y = C + I + Thou + (Ten-M)[/latex]

Expenditure accounts: Components of the expenditure approach to calculating Gross domestic product every bit presented in the National Income Accounts (U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis).
Defining the components
Consumption
Consumption (C) is normally the largest Gross domestic product component in the economy, consisting of private (household final consumption expenditure) in the economy. These personal expenditures fall under one of the following categories: durable appurtenances, not-durable goods, and services. Examples include food, hire, jewelry, gasoline, and medical expenses but does not include the buy of new housing. Also, it is important to notation that appurtenances such as hand-knit sweaters are not counted as role of GDP if they are gifted and not sold. Merely expenditure based consumption is counted.
Investment
Investment (I) includes, for instance, business organization investment in equipment, merely does not include exchanges of existing assets. Examples include construction of a new mine, purchase of software, or buy of machinery and equipment for a factory. Spending by households (non authorities) on new houses is also included in Investment. In dissimilarity to mutual usage, 'Investment' in Gdp does non mean purchases of financial products. Ownership financial products is classified as ' saving ', as opposed to investment. This avoids double-counting: if one buys shares in a company, and the company uses the money received to buy plant, equipment, etc., the amount will be counted toward GDP when the company spends the money on those things. To count information technology when 1 gives it to the company would be to count ii times an corporeality that but corresponds to one group of products. Annotation that buying bonds or stocks is a swapping of deeds, a transfer of claims on future production, non directly an expenditure on products.
Regime Spending
Government spending (G) is the sum of regime expenditures on terminal goods and services. It includes salaries of public servants, buy of weapons for the military, and whatever investment expenditure past a government. It does not include whatsoever transfer payments, such as social security or unemployment benefits.
Net Exports
Exports (10) represents gross exports. Gdp captures the amount a country produces, including goods and services produced for other nations' consumption, therefore exports are added.
Imports (M) represents gross imports. Imports are subtracted since imported goods will exist included in the terms G, I, or C, and must be deducted to avoid counting foreign supply as domestic.
Sometimes, internet exports is just written as NX, simply is the aforementioned thing as X-M.
Note that C, Grand, and I are expenditures on final appurtenances and services; expenditures on intermediate goods and services practise not count.
Calculating GDP
GDP tin exist calculated through the expenditures, income, or output arroyo.
Learning Objectives
Identify the output approach to calculating Gross domestic product
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- The expenditures approach says Gross domestic product = consumption + investment + government expenditure + exports – imports.
- The income approach sums the cistron incomes to the factors of production.
- The output approach is also chosen the "net product" or "value added" approach.
Key Terms
- expenditure approach: The total spending on all concluding goods and services (Consumption goods and services (C) + Gross Investments (I) + Government Purchases (G) + (Exports (X) – Imports (Thousand)) Gross domestic product = C + I + Thou + (X-M).
- income approach: GDP based on the income arroyo is calculated past adding upwardly the factor incomes to the factors of product in the society.
- output approach: GDP is calculated using the output arroyo by summing the value of sales of appurtenances and adjusting (subtracting) for the buy of intermediate goods to produce the appurtenances sold.
Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product is one method of agreement a country'due south income and allows for comparison to other countries.

Global GDP: GDP is a mutual measure for both inter-country comparisons and intra-country comparisons. The metric is 1 method of agreement economical growth within a country's borders.
Past calculating the value of goods and services produced in a country, Gdp provides a useful metric for understanding the economic momentum between the major factors of an economic system: consumers, firms, and the authorities. There are a few methods used for calculating GDP, the well-nigh commonly presented are the expenditure and the income approach. Both of these methods calculate Gross domestic product by evaluating the concluding stage of sales (expenditure) or income (income). However, some other approach referred to equally the "output approach" calculates Gdp past evaluating the value of all sales and adjusting for the purchase of intermediate goods (to remove double counting).
Expenditures Approach
The nearly well known approach to computing Gross domestic product, the expenditures approach is characterized past the following formula:
GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
where C is the level of consumption of goods and services, I is gross investment, G is government purchases, X is exports, and M is imports.
Income Approach
The income arroyo adds upwards the factor incomes to the factors of production in the gild. Information technology can be expressed as:
Gdp = National Income (NY) + Indirect Business Taxes (IBT) + Uppercase Consumption Allowance and Depreciation (CCA) + Cyberspace Factor Payments to the rest of the world (NFP)
Output Approach
The output approach is too chosen "net production" or "value added" method. This method consists of three stages:
- Estimating the gross value of domestic output;
- Determining the intermediate consumption, i.eastward., the price of cloth, supplies, and services used to produce last goods or services;
- Deducting intermediate consumption from gross value to obtain the net value of domestic output.
Net value added = Gross value of output – Value of intermediate consumption.
Gross value of output = Value of the full sales of goods and services + Value of changes in the inventories.
The sum of net value added in various economic activities is known every bit Gross domestic product at cistron cost. GDP at factor cost plus indirect taxes less subsidies on products is Gross domestic product at producer price. GDP at producer price theoretically should be equal to Gdp calculated based on the expenditure approach. All the same, discrepancies do arise because in that location are instances where the price that a consumer may pay for a adept or service is not completely reflected in the amount received by the producer and the revenue enhancement and subsidy adjustments mentioned higher up may non adequately adapt for the variation in payment and receipt.
Other Approaches to Calculating Gross domestic product
The income arroyo evaluates GDP from the perspective of the final income to economic participants.
Learning Objectives
Explain the income approach to calculating Gross domestic product.
Key Takeaways
Primal Points
- The sum of COE, GOS, and GMI is called total factor income; information technology is the income of all of the factors of product in society. It measures the value of Gross domestic product at factor (basic) prices.
- Calculation taxes less subsidies on production and imports converts GDP at cistron cost (as noted, a cyberspace domestic production) to GDP.
- By definition, the income approach to calculating Gdp should exist equatable to the expenditure arroyo; however, measurement errors volition make the ii figures slightly off when reported past national statistical agencies.
Key Terms
- income approach: GDP based on the income approach is calculated by adding upwards the factor incomes to the factors of product in the society.
- expenditure approach: The full spending on all final goods and services (Consumption goods and services (C) + Gross Investments (I) + Regime Purchases (Yard) + (Exports (X) – Imports (Thousand)) Gross domestic product = C + I + M + (Ten-G).
- depreciation: The measurement of the decline in value of assets. Non to be confused with damage, which is the measurement of the unplanned, extraordinary decline in value of assets.
Gross domestic product provides a measure out of the productivity of an economy specific to the national borders of a country. Information technology tin be measured a few unlike ways and the most commonly used metric is the expenditure approach; however, the second about commonly used measure is the income arroyo. The income approach dissimilar the expenditure approach, which sums the spending on terminal goods and services across economical agents (consumers, businesses and the government), evaluates Gross domestic product from the perspective of the final income to economic participants. GDP calculated in this style is sometimes referenced equally "Gross Domestic Income" (GDI).
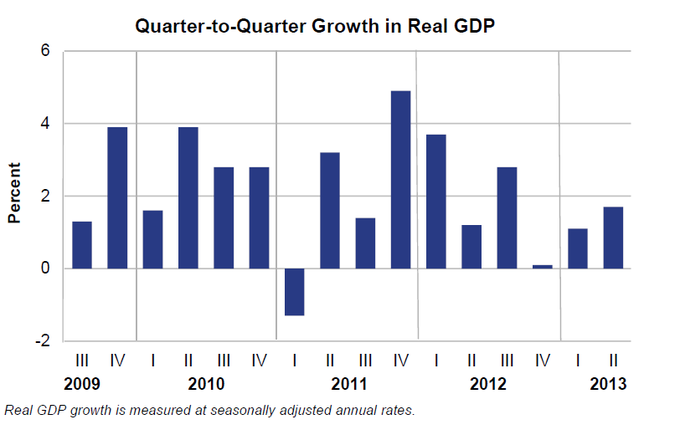
GDP over time: GDP is measured over consecutive periods to enable policymakers and economical agents to evaluate the country of the economy to set expectations and brand decisions.
This method measures GDP by calculation incomes that firms pay households for factors of production they hire- wages for labor, interest for majuscule, rent for land, and profits for entrepreneurship. The U.S. "National Income and Expenditure Accounts" divide incomes into five categories:
- Wages, salaries, and supplementary labor income
- Corporate profits
- Interest and miscellaneous investment income
- Farmers' income
- Income from non-farm unincorporated businesses
Ii adjustments must be fabricated to get the GDP: Indirect taxes minus subsidies are added to become from gene toll to market place prices. Depreciation (or Capital Consumption Assart) is added to get from cyberspace domestic product to gross domestic product.
Income Approach Formula
Gdp = compensation of employees + gross operating surplus + gross mixed income + taxes less subsidies on production and imports. Alternatively, this tin exist expressed every bit:
GDP = COE + GOS + GMI + TP & M – SP & M
- Compensation of employees (COE) measures the full remuneration to employees for piece of work washed.
- Gross operating surplus (GOS) is the surplus due to owners of incorporated businesses.
- Gross mixed income (GMI) is the same measure out as GOS, simply for unincorporated businesses. This often includes most modest businesses.
- TP & M is taxes on production and imports.
- SouthwardP&M is subsidies on product and imports.
The sum of COE, GOS, and GMI is chosen full factor income; it is the income of all of the factors of production in society. It measures the value of GDP at factor (basic) prices. The departure between basic prices and final prices (those used in the expenditure adding) is the full taxes and subsidies that the authorities has levied or paid on that production. So, adding taxes less subsidies on production and imports converts Gross domestic product at factor toll (as noted, a net domestic product) to Gdp.
By definition, the income approach to computing GDP should be equatable to the expenditure approach (Y = C + I+ Chiliad + (X – M)). In exercise, all the same, measurement errors will make the two figures slightly off when reported by national statistical agencies.
Evaluating GDP equally a Measure of the Economy
The value of GDP as a measure of the quality of life for a given country may be limited.
Learning Objectives
Assess the uses and limitations of GDP as a measure of the economy
Cardinal Takeaways
Key Points
- The sensitivities related to social welfare has continued the argument specific to the use of Gdp as a economic growth or progress metric.
- A country with broad disparities in income could announced to be economically stronger, strictly using GDP, than a country where the income disparities were significantly lower (standard of living).
- Therefore, Gdp has a tremendous big-picture value just policymakers would be better served using other metrics in combination with the aggregate mensurate if and when social welfare is being addressed.
Key Terms
- qualitative: Based on descriptions or distinctions rather than on some quantity.
- welfare: Health, safety, happiness and prosperity; well-beingness in any respect.
- quantitative: Of a measurement based on some number rather than on some quality.
Gross domestic production (GDP) due to its relative ease of calculation and definition, has go a standard metric in the word of economic welfare, growth and prosperity. However, the value of Gdp as a measure of the quality of life for a given land may be quite poor given that the metric only provides the total value of production for a specific time interval and provides no insight with respect to the source of growth or the beneficiaries of growth. Therefore, growth could be misinterpreted by looking at GDP values in isolation.
Limitations of GDP
Simon Kuznets, the economist who developed the get-go comprehensive set of measures of national income, stated in his first report to the US Congress in 1934, in a section titled "Uses and Abuses of National Income Measurements":
"Economical welfare cannot exist adequately measured unless the personal distribution of income is known. And no income measurement undertakes to estimate the opposite side of income, that is, the intensity and unpleasantness of effort going into the earning of income. The welfare of a nation tin, therefore, scarcely be inferred from a measurement of national income. "
Post-obit on his caution with respect to economic extrapolations from Gross domestic product, in 1962, Kuznets stated: "Distinctions must be kept in listen between quantity and quality of growth, between costs and returns, and between the short and long run. Goals for more growth should specify more growth of what and for what. "
The sensitivities related to social welfare has continued the statement specific to the use of Gdp as a economical growth or progress metric.
Austrian Schoolhouse economist Frank Shostak has noted: "The Gdp framework cannot tell us whether final appurtenances and services that were produced during a item period of time are a reflection of real wealth expansion, or a reflection of capital consumption. For example, if a government embarks on the building of a pyramid, which adds admittedly nothing to the well-existence of individuals, the Gdp framework will regard this equally economical growth. In reality, still, the building of the pyramid will divert existent funding from wealth-generating activities, thereby stifling the production of wealth."
GDP as an Evaluation Metric
Although GDP provides a unmarried quantitative metric by which comparisons can be fabricated beyond countries, the aggregation of elements that create the single value of Gdp provide limitations in evaluating a state and its economic agents. Given the calculation of the metric, a country with wide disparities in income could appear to be economically stronger than a state where the income disparities were significantly lower (standard of living). However, a qualitative assessment would likely value the latter country compared to the sometime on a welfare or quality of life ground.

GDP across the world: Gross domestic product can be adjusted to compare the purchasing power across countries but cannot exist adjusted to provide a view of the economic disparities inside a country.
Therefore, GDP has a tremendous large-motion-picture show value but policymakers would be better served using other metrics in combination with the amass measure if and when social welfare is being addressed.
lirettecapecrom45.blogspot.com
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-economics/chapter/measuring-output-using-gdp/
0 Response to "Gdp Can Be Calculated by Summing Up the "Value Added" at Every Stage of Production."
Post a Comment